Brief Introduction To Child Marriage:
Child marriage, a centuries-old tradition, persists globally, including India. It is primarily practiced by religious groups, attributing religious significance to the custom. Efforts are needed to raise awareness, promote education, and advocate for legal reforms to protect the rights of young girls. In addition to this, poverty and lack of awareness also play a major role in this issue. The perpetuation of child marriage can be attributed to individuals who have themselves experienced forced early marriages within their own families, thus continuing the cycle. Child marriage impacts a variety of areas of life such as education, health, livelihood and overall development of an individual’s personality.
History Of This Awkward Social Practice:
Women’s Rights: From Equality to Struggle:
During the early Vedic period, women enjoyed education, civilization, equal rights to men, and held esteemed social status, reflecting a more egalitarian society. However, with the advent of the Sutra period, women’s high status began to deteriorate (600-300 B.C.). During the Sangam period, Tamil Nadu’s women were well-treated and held high social status. During the Vijayanagar period, women had a good social standing and occupied an honorable position. Raja Ram Mohan Roy was the first man to advocate for women’s rights, who stands out for interpreting the East in light of the West. Child marriage became a cause for organizations such as the Brahmo Samaj and the Arya Samaj. Government should introduce a special law to protect the child wife from the physical abuse and harassments.
Reformers Challenge Traditional Marriage Norms:
The first step in this direction was taken in 1860 at the request of Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar. Later reformers such as Keshab Chandra Sen and Behramji Malabari considered this age to be too young. Keshab Chandra Sen of the Brahmo Samaj introduced a novel marriage ceremony, requiring the consent of the bride-groom and bride to form a union that recognized women’s individuality and ceased to be a contract between parents and children. Furthermore, marriage ceremonies could now be performed without regard to caste, creed, or religion. Sen also sent circulars to medical authorities in order to determine the marriageable age. He initiated a campaign against child marriage, leading to its prohibition under the Brahmo Act 1872, also referred to as the Native Marriage Act.
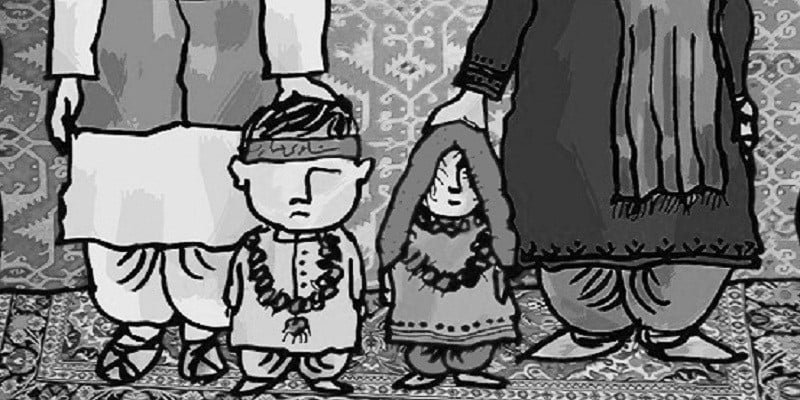

Detailed Analysis Of Child Marriage:
Factors Motivating Child Marriages:
The role of women lies at the crossroads between production and reproduction, economic activity and providing for the human needs of the family. They are workers in both spheres but face widespread discrimination. Gender discrimination permeates various aspects of society, such as education, employment, work environments, family dynamics, and the socio-political sphere. Child marriage is an example of discrimination against women.
Avoiding Expenditure On Female Education:
The society is discriminating between female children and male children in the investment of education. Male children are treated as the future asset for their family, while female children are often considered a burden. This has led to an imbalance in the gender ratio of graduates, with only one out of five being girls. It has also led to a decline in female employment rates, with half of working-age women not employed.
Avoiding Share In Ancestral Property:
Female children face discrimination regarding ancestral property inheritance, often being deprived of their rightful share. In this section, we discuss how there are some reasons behind it. Inheritance rights of female children have been withheld throughout history. There are many reasons for this happening. There are two primary reasons for the discrimination against women: cultural norms that determine behavior and limited access to education in certain regions.
Poverty Of Family:
Poor families are selling girls and the child marriage is a hidden form of selling girl child. Failure of Society, Government, and Law to Protect Young Girls from Early Marriages
Social Insecurity:
Social security is also one of the social factors responsible for child marriage system. In India it’s a meagre amount and some people who are unable to sustain their families, they depend on the elders and the children.
Single Parent Families:
Some of the families of our country are single parent families, which compel them to reduce the burden by performing marriage to their below 18 years girl child. It is only considered as an excuse.

Law And Government Initiatives:
Provisions Of The Prohibition Of Child Marriage Act, 2006:
To avoid the ineffectiveness of Child Marriage Restraint Act, 1929, the new Act increased the minimum marriageable age of female to 18 years and of male to 21 years respectively. The legislation has enabling provisions that prohibit child marriages, protect and provide relief to victims, and impose enhanced punishment for those who abet, promote, or solemnize such marriages.
Conclusion:
Elimination of early marriage is a clear starting point. The outcomes from this study suggest the following strategies to address this problem:
- Challenge the traditions that surround early marriage. Inform parents, community members, and youth about the negative consequences of early marriage.
- Create a supportive network of (religious) leaders and teachers who can empower girls to negotiate with their parents.
- Expand training for health and community workers on the dangers of early marriage. They engaging them as advocates and change agents in their communities and institutions.
- Strengthen and establish community networks and partnerships involving girls clubs, teachers, elders, local government officials, women and youth groups, community and religious leaders, etc., that jointly work towards ending early marriage.
- Strengthen the role of the judicial system particularly the police, judges and persecutors through training on enforcement of the law against early marriage.
- Develop strong support systems to keep girls in school. Provide scholarships where necessary and encourage teachers to support girls.
- Bring leading professional women to communities to talk to girls as role models and a source of inspiration.
Finally, given the factors motivating child marriages, all efforts should aim at changing the gender biased attitudes of parents and society by imparting proper education on one hand and eradicating poverty on the other.
**********
Disclaimer:- Views expressed are the author’s own.